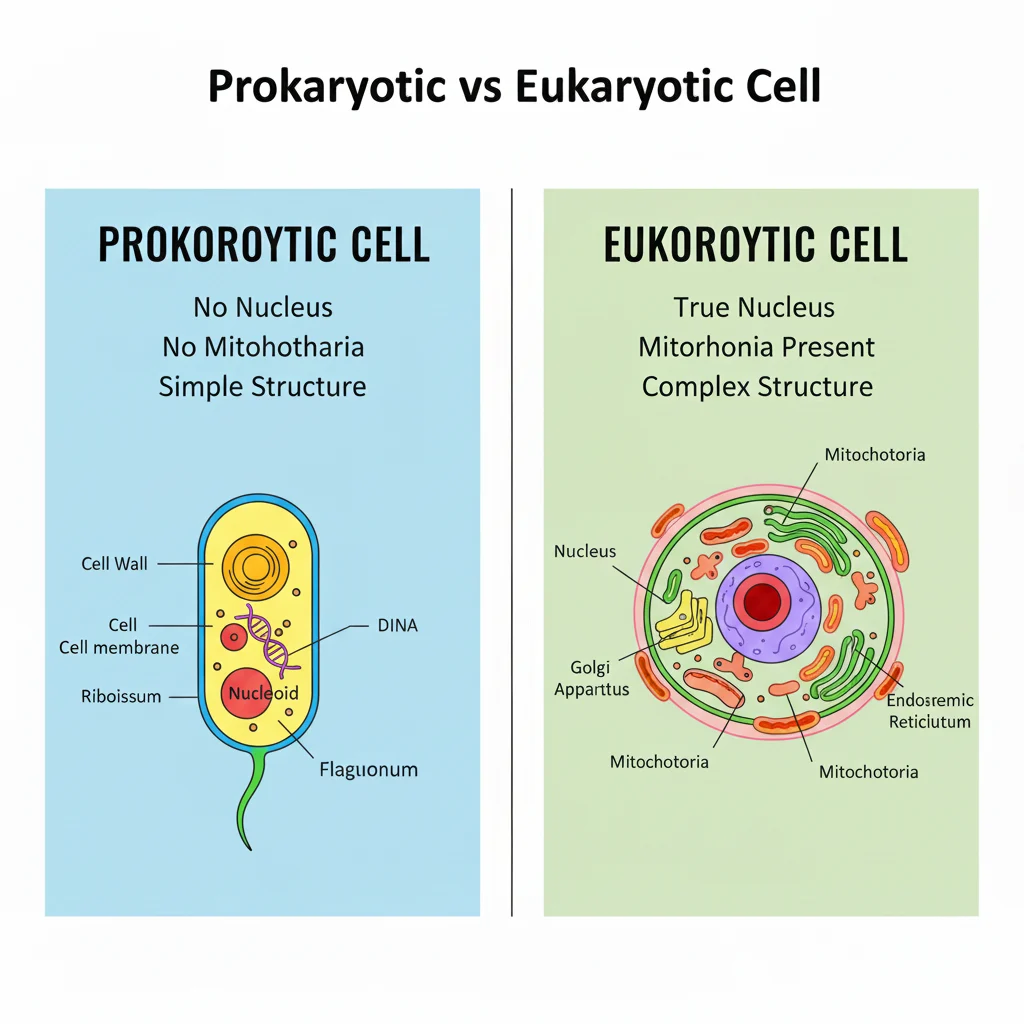
Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells, not prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells do not have mitochondria. Eukaryotic cells do have mitochondria because they are complex cells with membrane-bound parts.
If you remember just one line, remember this:
👉 Mitochondria = Eukaryotic cells only
Many students ask the same question again and again:
“Mitochondria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?”
This confusion is very common, especially for beginners. The words prokaryotic and eukaryotic sound similar, and mitochondria are tiny, so it’s easy to mix things up.
In this simple guide, you will learn:
- What mitochondria are
- What prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells mean
- The key difference between them
- Easy examples you can remember
- Common mistakes and how to avoid them
This article is written in plain English, with short sentences and real-life examples. Even a class 4 student can understand it easily.
Let’s make biology simple and fun 😊
What Does Each Word Mean?
What Are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are tiny parts inside a cell that make energy.
Think of mitochondria as:
👉 Power plants of the cell
They give the cell energy so it can grow, move, and stay alive.
Part of speech:
- Noun (name of a thing)
Easy Examples:
- Mitochondria help the cell make energy.
- Muscle cells have many mitochondria.
- Without mitochondria, many cells cannot survive.
Simple Story:
A cell is like a house. Mitochondria are the electricity generators inside the house.
What Does Prokaryotic Mean?
Prokaryotic cells are very simple cells.
They:
- Do NOT have a nucleus
- Do NOT have mitochondria
- Are very small
Examples of prokaryotic cells:
- Bacteria
- Blue-green algae
Part of speech:
- Adjective (describes a noun)
Easy Examples:
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells are very simple.
- Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria.
What Does Eukaryotic Mean?
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells.
They:
- Have a nucleus
- Have mitochondria
- Have other cell parts
Examples of eukaryotic cells:
- Human cells
- Plant cells
- Animal cells
Part of speech:
- Adjective
Easy Examples:
- Human cells are eukaryotic.
- Eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria.
- Plants have eukaryotic cells.
The Key Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic (Mitochondria Focus)
🔍 Comparison Table
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Mitochondria | ❌ Not present | ✅ Present |
| Nucleus | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Cell Type | Simple | Complex |
| Examples | Bacteria | Humans, plants |
| Energy Source | Cell membrane | Mitochondria |
✅ Quick Tip to Remember
If a cell has mitochondria, it is eukaryotic.
No mitochondria? Then it is prokaryotic.
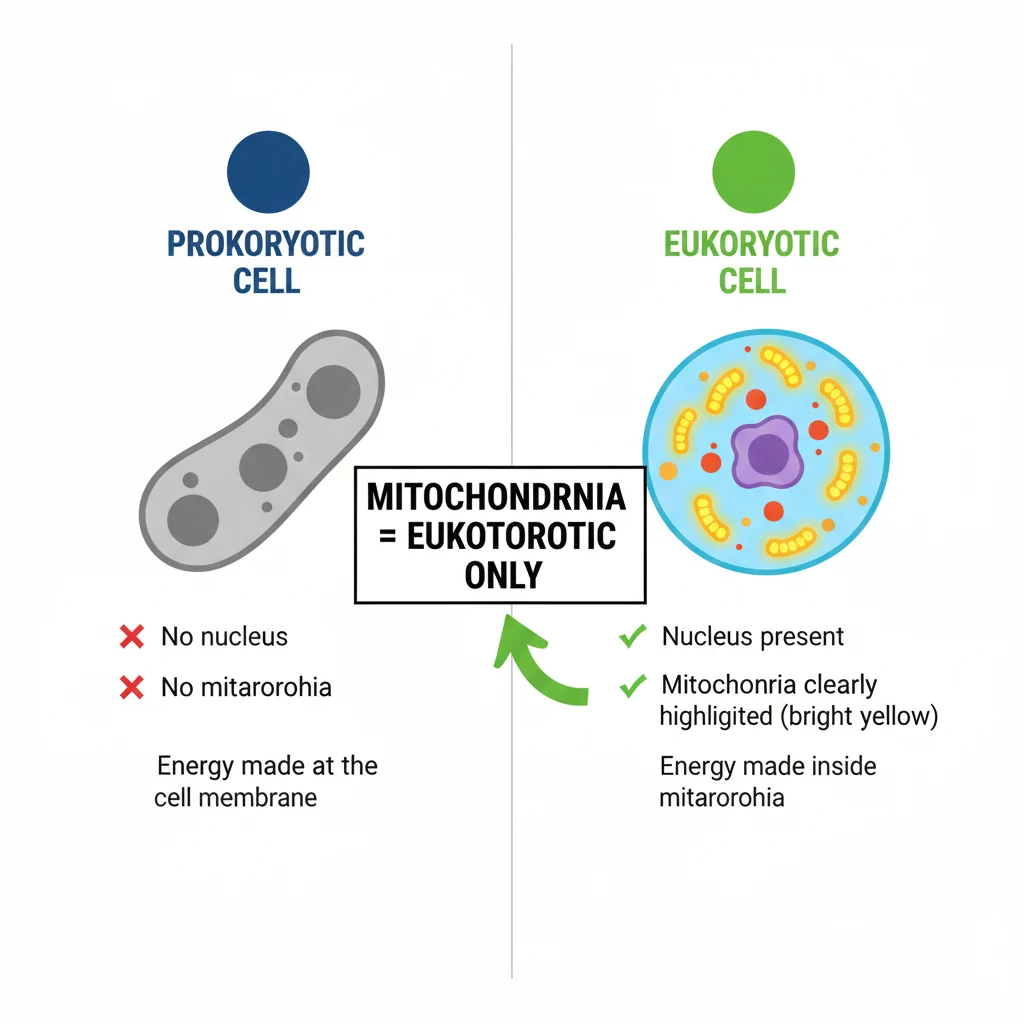
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
❌ Mistake 1:
Mitochondria are found in prokaryotic cells.
✅ Correct:
Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells.
Why it happens:
Students think all cells need mitochondria.
Fix:
Remember: Prokaryotes make energy without mitochondria.
❌ Mistake 2:
Bacteria have mitochondria.
✅ Correct:
Bacteria do not have mitochondria.
Why it happens:
Bacteria are alive, so people think they need mitochondria.
Fix:
Bacteria are prokaryotic → no mitochondria.
When to Use “Prokaryotic”
Use prokaryotic when talking about:
- Simple cells
- Cells without a nucleus
- Cells without mitochondria
Examples:
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells are very small.
- Prokaryotic cells lack mitochondria.
- Prokaryotes are simpler than eukaryotes.
Real Life Example:
When studying germs or bacteria, use prokaryotic.
When to Use “Eukaryotic”
Use eukaryotic when talking about:
- Human cells
- Plant or animal cells
- Cells with mitochondria
Examples:
- Human cells are eukaryotic.
- Mitochondria exist in eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic cells are complex.
- Plants are made of eukaryotic cells.
🧠 Memory Hack
EU = “You”
If the cell belongs to you (human), it is eukaryotic and has mitochondria.
Quick Recap: Mitochondria Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
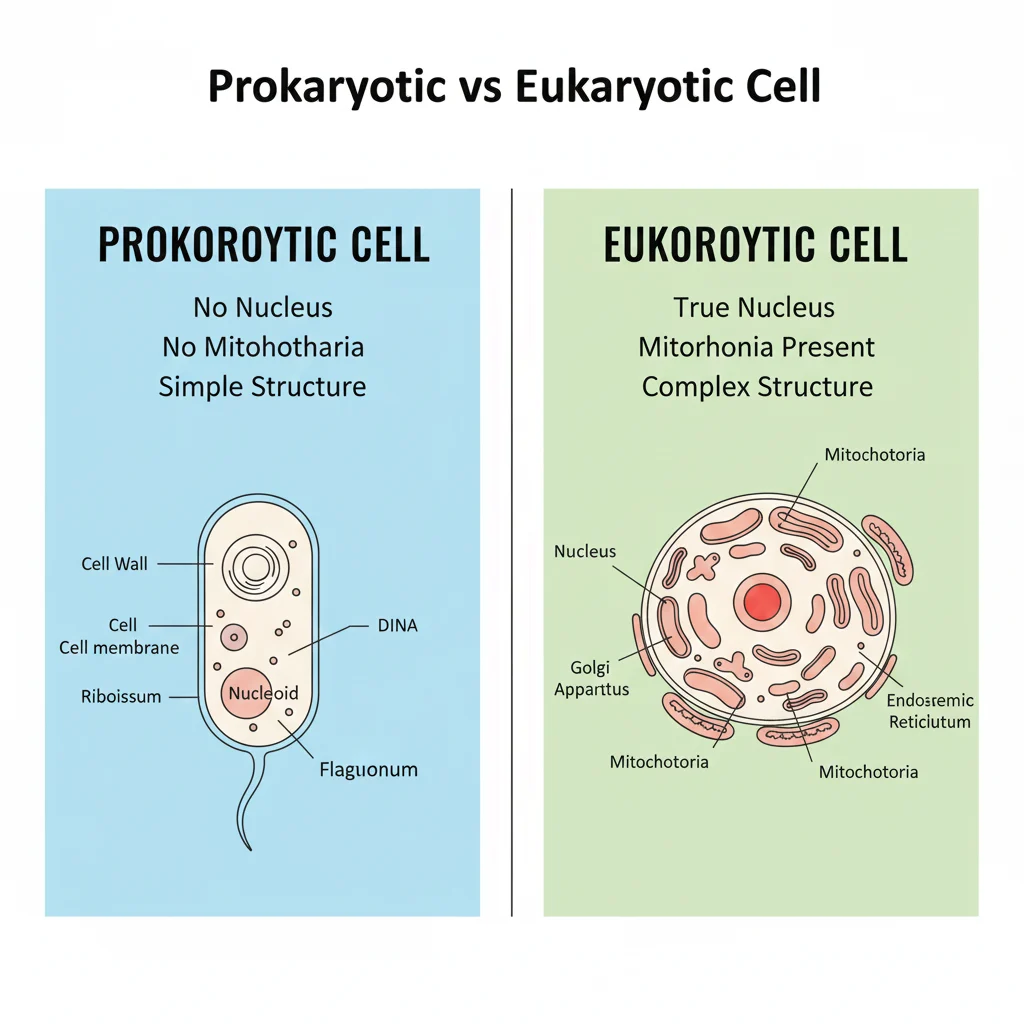
- ✅ Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells
- ❌ Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic = simple cells (bacteria)
- Eukaryotic = complex cells (humans, plants)
One-line rule:
👉 Mitochondria = Eukaryotic
Advanced Tips
- The word mitochondria comes from Greek words meaning thread and granule.
- In exams, always link mitochondria with eukaryotic cells.
- In online writing, mixing these terms can change the meaning and reduce marks.
- Formal biology writing always states: Prokaryotic cells lack mitochondria.
📝 Mini Quiz: Test Yourself
Fill in the blanks:
- Mitochondria are found in __________ cells.
- Bacteria are __________ cells.
- Prokaryotic cells do not have __________.
- Human cells are __________.
- The power plant of the cell is __________.
✅ Quiz Answers
- Eukaryotic
- Prokaryotic
- Mitochondria
- Eukaryotic
- Mitochondria
❓ FAQs
1. Are mitochondria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Mitochondria are eukaryotic.
2. Do prokaryotic cells have mitochondria?
No, they do not.
3. Why don’t prokaryotes have mitochondria?
They are simple cells and make energy differently.
4. Are human cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Human cells are eukaryotic.
5. What is the easiest way to remember this?
Mitochondria = Eukaryotic cells only.
Conclusion
Now you clearly know the answer to the big question:
Mitochondria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Mitochondria belong to eukaryotic cells, not prokaryotic ones. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria are simple and do not have mitochondria. Eukaryotic cells, like human and plant cells, are complex and need mitochondria to make energy.
Keep practicing with examples, tables, and memory tricks. Little steps like this help you improve your science and English every day. Learning can be simple and fun — one concept at a time 🌟

Isla Merrin is a language and writing expert at Definevs.com, creating simple, engaging guides to help readers master words, grammar, and modern English usage.