Energy can be potential or kinetic depending on whether it is stored or moving.
Kinetic energy = energy of movement (anything that is moving).
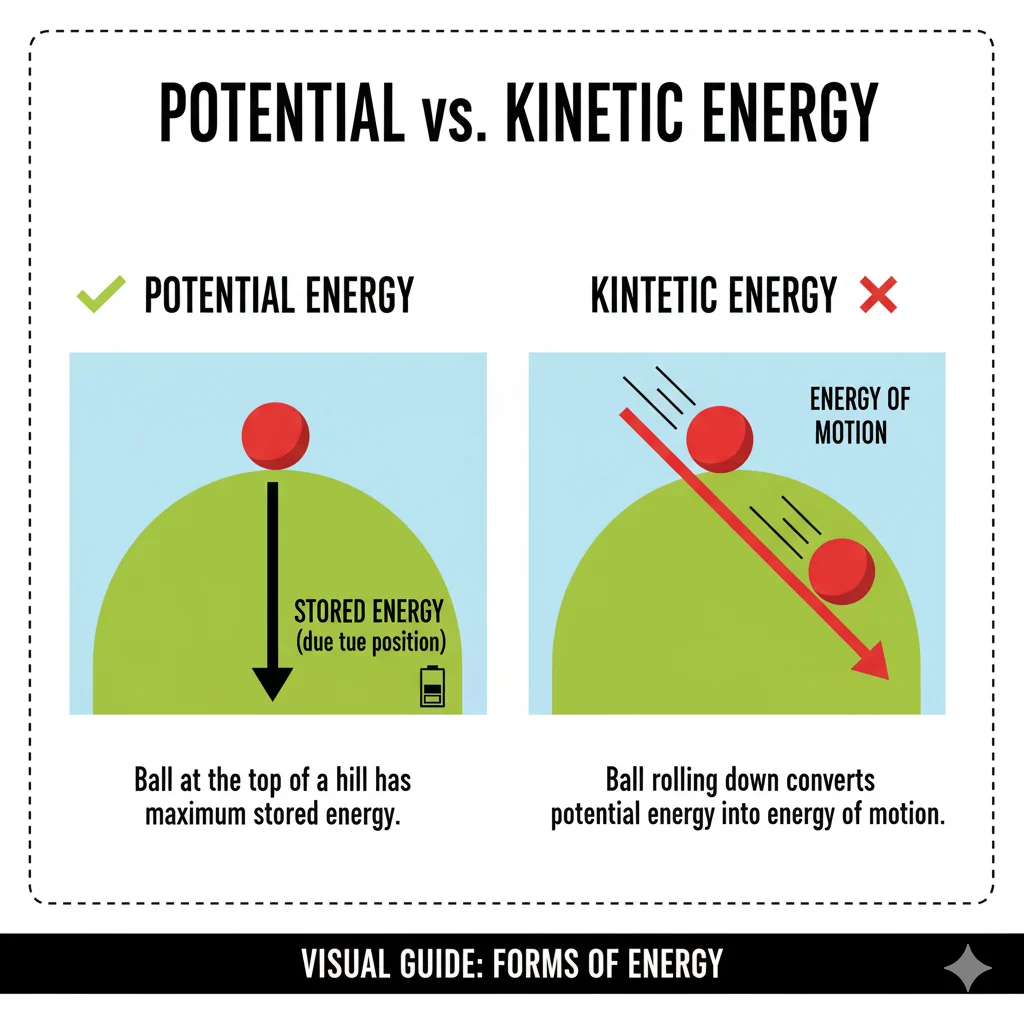
Potential energy = stored energy (not moving yet).
Have you ever asked yourself, “Is energy potential or kinetic?” Many students mix up these two terms because they sound scientific, similar, and a bit confusing. But the truth is: anyone — even a child — can understand them with simple examples and clear explanations.
In this guide, you will learn:
- What potential energy really means
- What kinetic energy really means
- The difference between potential and kinetic energy
- How to know which one to use in science questions
- Easy examples, memory tricks, and a comparison table
By the end, you will confidently understand the two types of energy and never mix them again. Let’s make science simple!
What Does Each Word Mean? (Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy)
Potential Energy (Meaning)
Potential energy means stored energy — energy that an object has because of its position or condition.
Simple examples:
- A book on a shelf (it’s not moving, but it can fall).
- Water stored behind a dam.
- A stretched rubber band ready to snap.
Kinetic Energy (Meaning)
Kinetic energy means moving energy — energy that an object has because it is in motion.
Simple examples:
- A running dog.
- A rolling ball.
- A moving car.
The Key Difference Between Potential and Kinetic Energy
Comparison Table: Potential vs Kinetic Energy
| Feature | Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Stored energy | Energy of motion |
| Object State | Not moving | Moving |
| Depends On | Position or condition | Speed or movement |
| Example | A rock at the top of a hill | A rock rolling down the hill |
| Memory Trick | P = “paused energy” | K = “kicking/kinetic = moving” |
Quick Tip to Remember
- Potential = Possible movement (not yet happening).
- Kinetic = Movement happening right now.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Thinking potential energy is “unused kinetic energy.”
❌ Incorrect: “Potential energy is just kinetic energy waiting to happen.”
✔ Correct: Potential energy is stored energy, not moving energy.
Mistake 2: Calling something “kinetic” even when it’s still.
❌ Incorrect: A parked car has kinetic energy.
✔ Correct: A parked car has potential, not kinetic.
Mistake 3: Confusing height with speed.
Height = potential
Speed = kinetic
When to Use Potential Energy
Use potential energy when something is:
- Not moving
- Stored or held in place
- At a height or stretched or compressed
Examples:
- A glass sitting on a table.
- A bow pulled back before shooting an arrow.
- A kid sitting at the top of a slide.
- A battery storing chemical energy.
- A snowball resting on top of a hill.
When to Use Kinetic Energy
Use kinetic energy when something is:
- Moving
- Changing position
- Speeding up or slowing down
Examples:
- A boy riding a bicycle.
- Rain falling from the sky.
- A ball bouncing across the floor.
- A river flowing fast.
- A car driving on a road.
Memory Hack
Think: Kinetic = Kicking = Movement.
Anything that is moving has kinetic energy.
Quick Recap: Potential vs Kinetic Energy
- Potential = stored, not moving
- Kinetic = moving, active
- Potential energy can change into kinetic energy (like a falling object).
- Kinetic energy can change back into potential (like when something moves upward and slows down).
Advanced Tips
Origin of the Words
- Potential comes from “potent,” meaning “powerful or possible.”
- Kinetic comes from the Greek word kinesis, meaning “motion.”
In Formal Writing or Exams
Use clear terms:
- “The object has potential energy due to its height.”
- “The object has kinetic energy because it is moving.”
In Real Life
- Roller coasters use both: going up (potential), going down (kinetic).
- Sports use both: a football held (potential), a football kicked (kinetic).
Mini Quiz — Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks:
- A ball sitting on a table has ______ energy.
- A flying airplane has ______ energy.
- A stretched spring has ______ energy.
- A running cat has ______ energy.
- Water falling from a waterfall has ______ energy.
(Answers: 1. potential, 2. kinetic, 3. potential, 4. kinetic, 5. kinetic)
FAQs
1. Is energy potential or kinetic in real life?
Energy can be both. If an object is still, it has potential energy. If it is moving, it has kinetic energy.
2. What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored, kinetic energy is moving. One is calm, the other is active.
3. Can potential energy become kinetic energy?
Yes. When something starts moving (like a falling object), potential energy turns into kinetic energy.
4. Can an object have both types of energy?
Yes. A thrown ball has potential energy (height) and kinetic energy (movement) at the same time.
5. Why is height related to potential energy?
Because the higher something is, the more stored energy it has due to gravity.
Conclusion
Now you clearly understand the difference between potential and kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy, while kinetic energy is movement energy. With simple examples, real-life stories, and memory tricks, you can now easily decide which type of energy is being used in any situation.
Keep practicing with everyday objects — the more you observe, the faster you’ll learn. You’re improving your science skills every day!

Isla Merrin is a language and writing expert at Definevs.com, creating simple, engaging guides to help readers master words, grammar, and modern English usage.









