Ever seen the “≤” sign in math problems and wondered what it really means? 🤔
People often mix up “less than” (<), “greater than” (>), and “equal or less than” (≤) because they look similar — but each has a specific meaning.
In this simple guide, we’ll explain:
- What the equal or less than sign (≤) means
- How it’s different from less than (<) and equal (=)
- When and how to use it correctly in math and real life
- Common mistakes and easy memory tricks to remember
By the end, you’ll never get confused between these signs again!
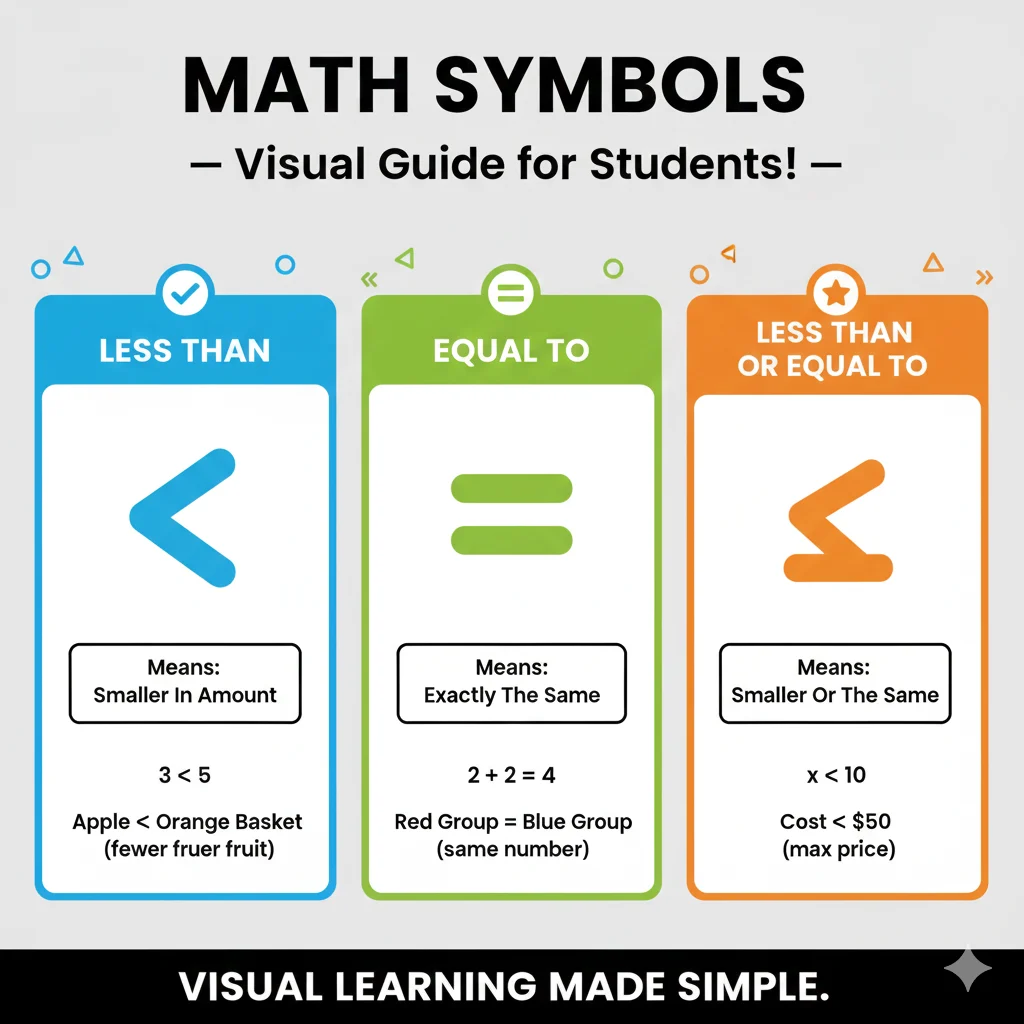
🔍 What Does Each Sign Mean?
Let’s start with the basics — understanding what each of these mathematical signs means.
➕ The Equal Sign (=)
Meaning: Shows that two values are exactly the same.
Example Sentences:
- 4 = 4 (Both sides are equal.)
- 10 = 10 (They have the same value.)
- 7 + 3 = 10 (The total is equal to 10.)
➖ The Less Than Sign (<)
Meaning: Shows that one value is smaller than another.
Example Sentences:
- 3 < 5 (Three is less than five.)
- 8 < 10 (Eight is smaller than ten.)
- 12 < 15 (Twelve is less than fifteen.)
⚖️ The Equal or Less Than Sign (≤)
Meaning: Means that a number is either smaller than or equal to another number.
Example Sentences:
- 5 ≤ 8 (Five is less than or equal to eight.)
- 9 ≤ 9 (Nine is equal to nine.)
- x ≤ 10 (x can be any number less than or equal to ten.)
💡 Simple Tip:
The sign ≤ is like saying, “You can go up to this number, but not over it.”
📊 The Key Difference Between < and ≤
| Sign | Name | Meaning | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
< | Less Than | One number is smaller than another | 3 < 5 | 3 is smaller than 5 |
≤ | Equal or Less Than | One number is smaller or exactly equal to another | 5 ≤ 8 | 5 is less, but if it’s equal, it still works |
✅ Quick Tip to Remember:
Think of ≤ as the less than sign wearing an equal hat!
It means “less than or equal to.”
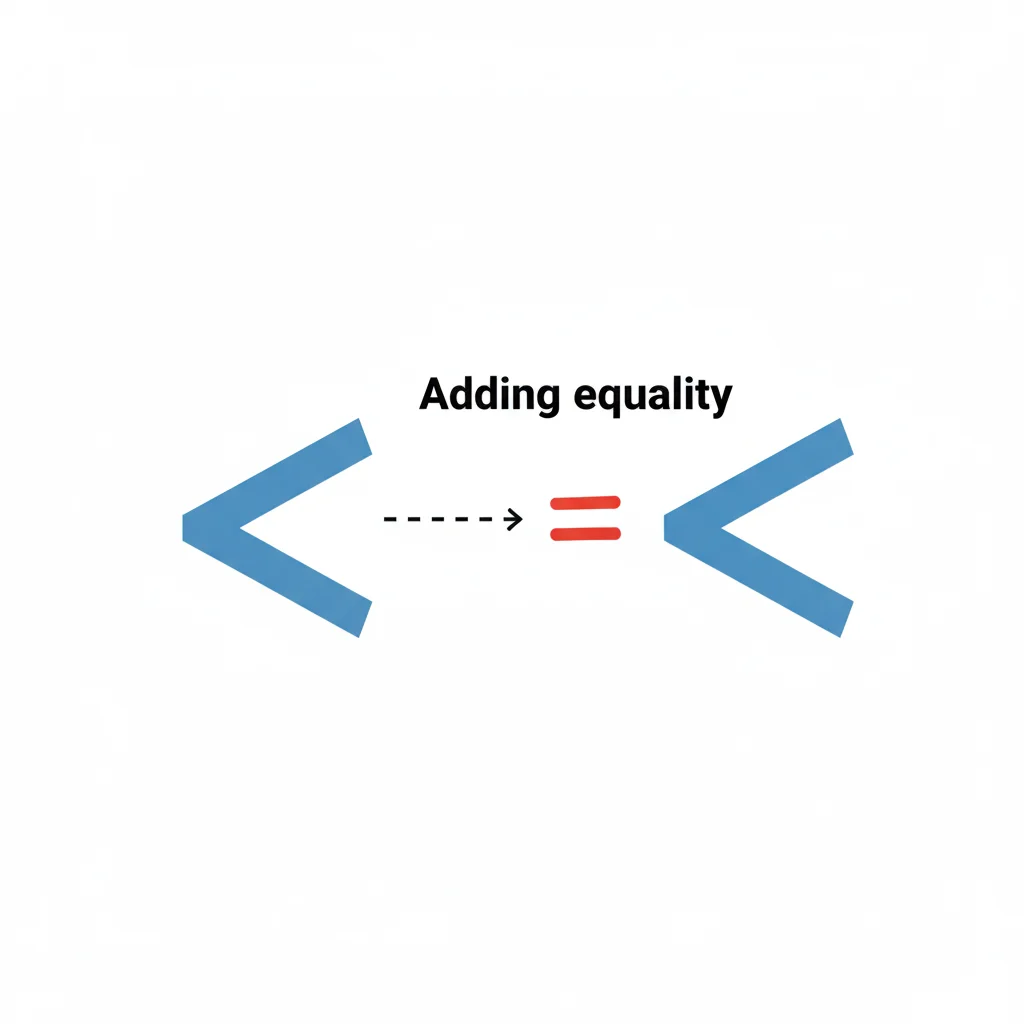
📸 Visual Suggestion:
Image showing “<” turning into “≤” by adding a tiny “=”, labeled “Adding equality.”
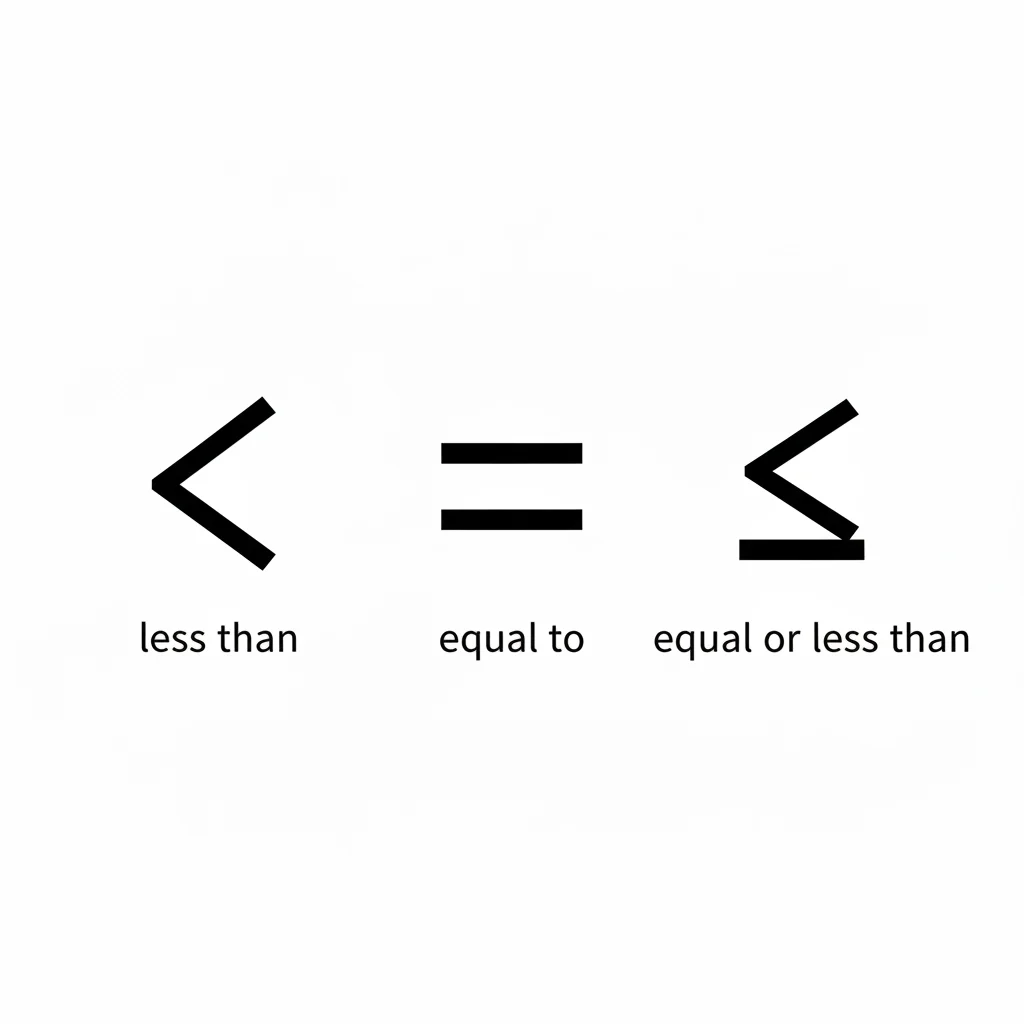
🚫 Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
❌ Mistake 1: Mixing up < and ≤
Incorrect: 5 < 5
Correct: 5 ≤ 5
Because 5 is equal, not smaller.
❌ Mistake 2: Using ≤ for everything
Incorrect: 3 ≤ 2
Correct: 3 > 2
Because 3 is greater, not smaller or equal.
❌ Mistake 3: Writing it backward
Incorrect: 7 ≥ 9 when you mean 7 ≤ 9.
Remember: The pointy end always faces the smaller number.
💡 Memory Hack:
The “mouth” of the sign (< or >) always opens toward the bigger number — it’s “hungry” for the larger value!
🧮 When to Use the Less Than Sign (<)
Use < when one value is smaller than another.
✅ Examples:
- 2 < 4 (Two is smaller than four.)
- Your test score (60) < Passing marks (70).
- The temperature today (10°C) < Yesterday (15°C).
- I have 3 candies < You have 5 candies.
- 100 < 200 (Simple comparison.)
💡 Real-Life Example:
If a game says “Only children under 12 can enter,” that means Age < 12 — anyone who is 12 or older cannot enter.
🧾 When to Use the Equal or Less Than Sign (≤)
Use ≤ when a number can be smaller than or exactly equal to another.
✅ Examples:
- x ≤ 10 means x can be 10, 9, 8, etc.
- You can carry ≤ 5 kg on the plane (up to 5 kg).
- Students with marks ≤ 50 need to retake the test.
- The price must be ≤ $20 to get a discount.
- Temperature ≤ 0°C means freezing or below.
💡 Memory Trick:
Think of the “equal or less than” sign as a double-duty symbol — it does two jobs: checking if something is smaller or exactly the same.
🧠 Quick Recap: Less Than (<) vs Equal or Less Than (≤)
- < means smaller only.
- ≤ means smaller or the same.
- The equal line (=) adds equality to the comparison.
✅ In short:
If equality matters → use ≤
If not → use <
Examples Recap:
- 4 < 6 ✅ (smaller only)
- 4 ≤ 6 ✅ (smaller or equal)
- 6 ≤ 6 ✅ (equal is okay)
- 7 < 7 ❌ (not smaller)
📸 Visual Suggestion:
An infographic with a simple number line showing where “<” and “≤” apply.
📚 Advanced Tips: How and Where It’s Used
1. In Mathematics
Used in equations, inequalities, and graphs.
Example: y ≤ 3 means “all points below or on the line y = 3.”
2. In Real Life
- Shopping limits (Spend ≤ $100)
- Age restrictions (Age ≤ 18)
- Weight limits (≤ 20 kg baggage)
- Grades or scores (Marks ≤ 50 = Fail)
3. In Programming
Coders use <= (two characters) to mean “less than or equal to” because computers don’t use the symbol ≤.
Example (Python):
if x <= 10:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
🧩 Mini Quiz — Test Your Understanding
Fill in the blanks with < or ≤:
- 8 ___ 10
- 5 ___ 5
- 7 ___ 9
- 6 ___ 4
- x ___ 12
Answers:
- <
- ≤
- <
- (trick question!)
- ≤
❓ FAQs About the Equal or Less Than Sign
1. What does ≤ mean in math?
It means “less than or equal to” — a value can be smaller or exactly equal.
2. How do you type ≤ on a keyboard?
You can type it by pressing Alt + 243 (Windows) or using Insert → Symbol → ≤ (Word). In coding, it’s written as <=.
3. What’s the difference between < and ≤?
“<” means smaller only, while “≤” includes equality too.
4. Where do we use ≤ in real life?
It’s used in measurements, limits, age rules, and score comparisons — anywhere there’s an upper boundary.
5. How can I remember ≤ easily?
Think: “Less than, or equal to.” The “=” is a reminder that equality is included.
🏁 Conclusion
Now you know the difference between less than (<) and equal or less than (≤)!
Use < when something is smaller, and ≤ when it can be smaller or the same.
These little signs may look similar, but their meanings are powerful — they help you compare numbers, set limits, and understand math clearly.
Keep practicing with small examples daily, and soon you’ll spot the right sign instantly — for real!

Kael Donovan is a language enthusiast and writer at Definevs.com, simplifying complex words and grammar rules into fun, easy-to-understand guides for readers.