Have you ever stopped while writing and asked yourself, “Should I say began or begun?” 🤔
You’re not alone! These two words look and sound similar, but using the wrong one can easily confuse your reader. Both come from the verb “begin,” but they’re used in different grammar situations.
In this simple guide, you’ll learn:
- The meaning of began and begun
- The difference between them
- How to use each word correctly in sentences
- Common mistakes, memory tricks, and examples to make learning easy
By the end, you’ll never mix them up again — even if English isn’t your first language.
🧠 What Does Each Word Mean?
Let’s break down both words simply.
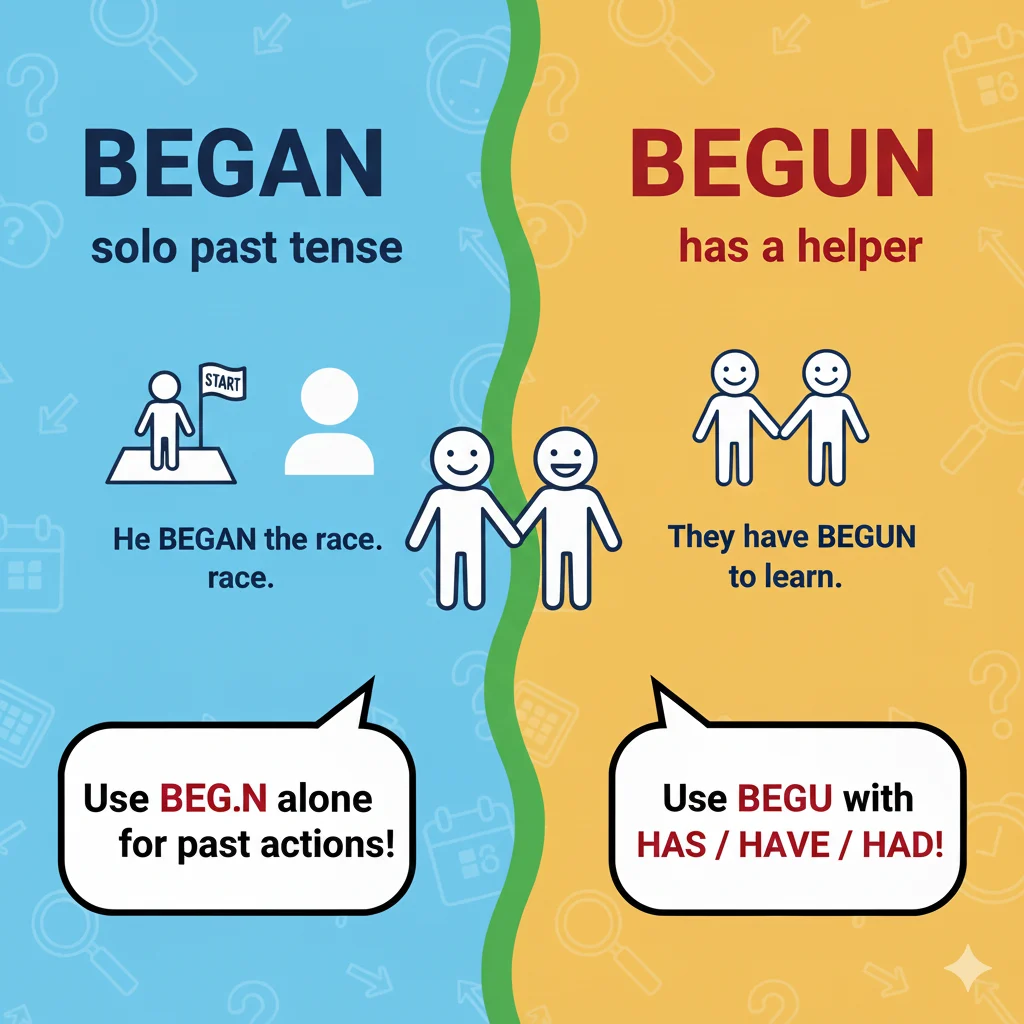
What Does “Began” Mean?
- Part of speech: Verb (past tense of begin)
- Meaning: It shows that something started or happened in the past.
- Used without “have,” “has,” or “had.”
Examples:
- The class began at 9 a.m.
- She began reading her favorite book yesterday.
- It began to rain before we got home.
👉 Think of “began” as the simple past — just like “ate” (from eat) or “ran” (from run).
What Does “Begun” Mean?
- Part of speech: Verb (past participle of begin)
- Meaning: It shows that something has started — usually with have, has, or had.
- Never used alone.
Examples:
- The movie has begun already.
- They had begun their journey before sunrise.
- It has begun to snow in the mountains.
👉 Think of “begun” as the partner of “have/has/had.”
Without those helper words, the sentence will sound incomplete.
Passed Away / Past Away: The Hidden Truth You Never Noticed 😮
⚖️ The Key Difference Between Began and Begun
Here’s the simplest way to remember:
| Feature | Began | Begun |
|---|---|---|
| Verb Form | Simple past | Past participle |
| Used With | No helper verbs | Always with have/has/had |
| Example | She began singing. | She has begun singing. |
| Meaning | Action already started in the past | Action started with a helper verb |
| Memory Tip | “Began” stands alone. | “Begun” needs a helper! |
💡 Quick Tip to Remember:
If there’s a “have,” “has,” or “had,” use begun.
If not, use began.
❌ Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even native speakers mix these two up! Let’s fix that.
❌ Incorrect:
- The show has began.
✅ Correct: - The show has begun.
(Because “has” needs the past participle form.)
❌ Incorrect:
- I had began learning guitar last year.
✅ Correct: - I had begun learning guitar last year.
(“Had” pairs with “begun.”)
❌ Incorrect:
- The rain begun suddenly.
✅ Correct: - The rain began suddenly.
(No “have/has/had,” so use “began.”)
👉 Grammar Tip: If you ever use “have,” “has,” or “had,” your word must end with “-un” — like begun, eaten, run, taken.
✏️ When to Use “Began”
Use “began” when the action happened in the past and is already finished.
Examples:
- The concert began an hour ago.
- We began our road trip early this morning.
- She began crying when she heard the news.
- The teacher began explaining the lesson.
- It began raining heavily during the match.
🧠 Memory Hack:
“Began” = “Before now.”
If the action is clearly in the past, use began.
🕓 When to Use “Begun”
Use “begun” when the action has started but the sentence includes a helping verb like have, has, or had.
Examples:
- The movie has begun.
- They had begun cleaning before guests arrived.
- It has begun to get cold outside.
- I have begun to enjoy cooking lately.
- The rain had begun before we left the house.
🧠 Memory Hack:
“Begun” always needs a buddy!
That buddy is have, has, or had.
🧾 Quick Recap: Began vs Begun
Here’s everything in a nutshell:
- Began = Past tense → Used for completed past actions.
- Begun = Past participle → Used with have/has/had.
- Began stands alone.
- Begun always has a helper.
- Began → Simple past; Begun → Perfect tenses.
🔹 Quick Memory Line:
Began yesterday.
Begun has help today!
💡 Advanced Tips
1. Origin of the Words
Both began and begun come from the Old English word “beginnan,” meaning “to start or open.” Over time, English changed how verbs show time, creating different forms — just like sing/sang/sung and run/ran/run.
2. In Formal Writing
In essays, reports, or exams, using the correct form shows strong grammar skills.
For example:
- “The meeting has begun on time.” (formal and correct)
- “The meeting began at 10 a.m.” (clear and correct for past time)
3. In Daily Conversation
People often say “began” and “begun” interchangeably, but that’s grammatically wrong.
Using the correct form helps you sound confident and fluent — whether you’re texting, writing an email, or speaking English naturally.
🧩 Mini Quiz: Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks with began or begun.
- The rain _______ just before we left.
- The teacher _______ the class with a joke.
- We _______ our journey early in the morning.
- It has _______ to snow outside.
- They had _______ their exams before the holidays.
- She _______ laughing after hearing the story.
Answers:
- begun
- began
- began
- begun
- begun
- began
Sung / Sang: The Hidden Grammar Detail Everyone Gets Wrong 😲
❓ FAQs
1. What’s the main difference between “began” and “begun”?
Began is the simple past tense, while begun is the past participle used with have, has, or had.
2. Can “begun” be used alone in a sentence?
No. Begun always needs a helping verb — have, has, or had.
3. Is “began” used in present tense?
No. Began refers to an action that already happened in the past.
4. How can I remember which to use?
If you see have/has/had, choose begun.
If not, use began.
5. Is “have began” correct grammar?
No. It should be “have begun.”
🏁 Conclusion
Now you know the clear difference between began and begun — and when to use each one correctly!
Remember: Began means something already started in the past, while begun works with helpers like have, has, or had.
Keep practicing by writing simple sentences daily — it’s the best way to master grammar naturally. You’ll be using these words confidently in no time! 🌟

Kael Donovan is a language enthusiast and writer at Definevs.com, simplifying complex words and grammar rules into fun, easy-to-understand guides for readers.









